Correlation of Texas Cone Penetrometer Test Values and Shear Strength of Texas Soils
Project PIs and Co-PIs
Dr. C. Vipulanadan, Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Houston
Dr. A. J. Puppala, Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Texas at Arlinton
Dr. Mien Jao, Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Lamar University
Short Description
In this study, Texas Cone Penetration test data of both field and laboratory tests conducted by the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) were collected, compiled, analyzed, and synthesized to create a database. Based on this database, correlation equations between blow-count and shear strength parameters were developed. In the development, the bearing capacity theory for low plasticity clay (CL soil) was adopted. The effectiveness of the new correlations was evaluated by comparing with what is currently being used by TxDOT.
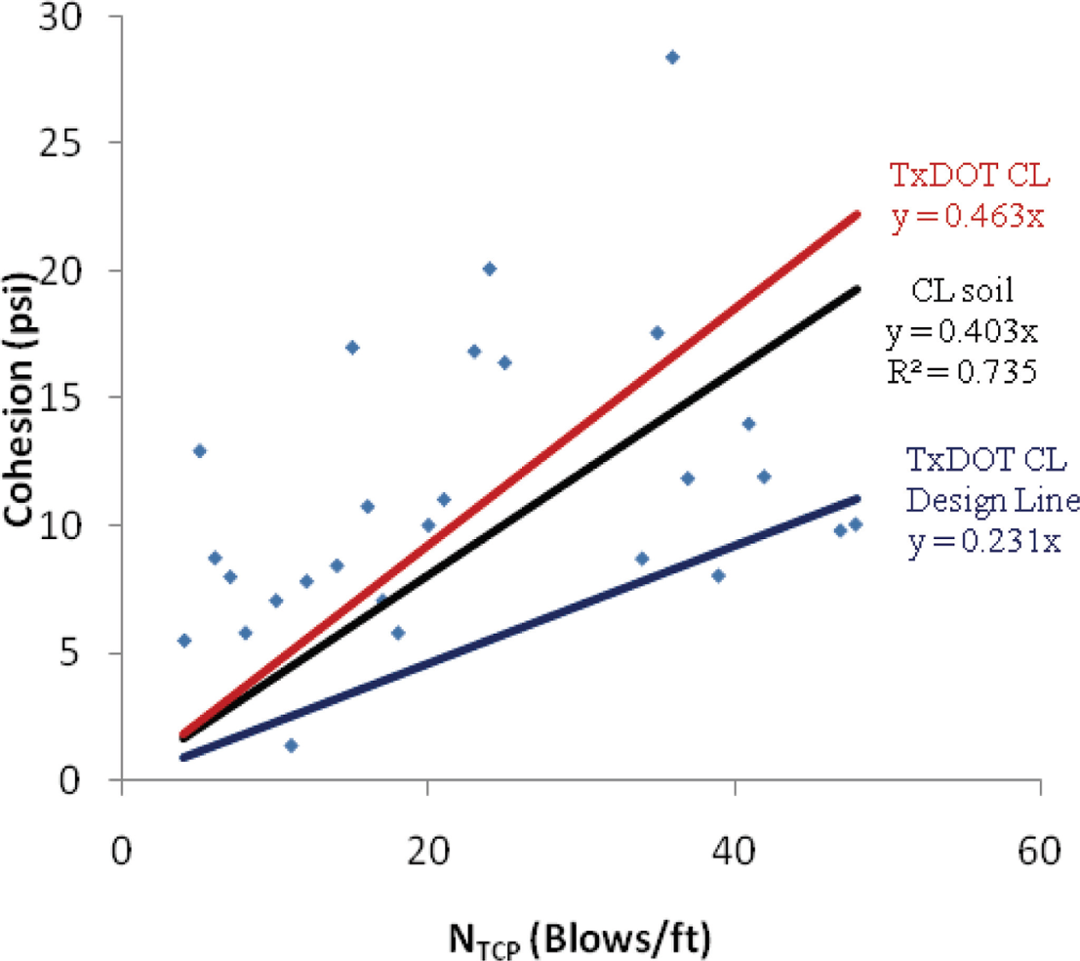
Full Description
Texas Cone Penetration test is a primary in-situ field test method for determining the shear strength of soils by the Texas Department of Transportation. For geotechnical analysis and foundation design, the available correlations between undrained cohesion and cone penetration blow count are not very effective for some soil and field conditions. In an attempt to compare/improve/refine the available correlations, this study was undertaken to investigate the effect of depth on cohesion vs. blow count relations. Based on the basic bearing capacity principle together with the statistical regression approach, the effect of depth on cohesion vs. blow count relation was developed. The TxDOT correlation was found to be close to the developed correlations for depths ranging between 15 ft (4.57 m) and 25 ft (7.62 m). It is concluded that the developed correlations with depth effect would be a good approach for improving the correlation currently used by TxDOT for geotechnical analysis and foundation design. However, it is recommended that more studies should be conducted in other types of soils in other TxDOT districts.
Funding
Funded by Texas Department of Transportation
Publications
- Nutan Palla, Suresh Gudavalli, Liang Chao, M. Jao,and M.C. Wang, “Numerical Analysis of Texas Cone Penetration Test”, International Journal of Applied Science and Technology, Vol.2, No.3, pp. 1-6, March 2012
- Palla, L. Chao, M. Jao, and M.C. Wang, “Correlating Undrained Shear Strength of Clay with Blow-Count of Texas Cone Penetrometer”, Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol.15, Bun. A, February 2010.
- S. Gudavalli, N. Palla, C. Vipulanadan, A. J. Puppala, M. Jao, X. Fang, S. Yin, and M.C. Wang, “Development of Correlation between TCP Blow Count and Undrained Shear Strength of Low Plasticity Clay”, Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization, April 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London, pp. 1401-1404.
- S. Kim, M. Jao, A. J. Puppala, P. Chang, S. Yin, I. Pannila and J. Delphia and C. Vipulanandan “Charactering the Soft Clays in the Texas Gulf Coase Using the Texas Cone Penetrometer (TCP)” Special Geotechnical Publication, No 173, New Peaks in Geotechnics, ASCE, February 2007.
- Vasudevan, A. J. Puppala, M. Jao, C. Vipulanandan, and S. Yin “Texas Cone Penetrometer (TCP) Correlations for Strength Predictions of Low Plasticity Clays” Special Geotechnical Publication, No. 149, Site and Geomaterial Characterization, ASCE, pp. 40 – 47, June 2006.
- C. Vipulanandan, A. J. Puppala, M. Jao, M. S. Kim, H. Vasudevan, and P. Kumar, “Correlation of Texas Cone Penetrometer Test Values and Shear Strength of Texas Soils” Final Project Report No. Texas Department of Transportation 0-4862, pp. 1-182, August 2006